What is VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a
network technology that creates a secure network connection over a public
network such as the Internet or a private network owned by a service provider.
Large corporations, educational institutions, and government agencies use VPN
technology to enable remote users to securely connect to a private network.
A VPN can connect multiple sites
over a large distance just like a Wide Area Network (WAN). VPNs are often used
to extend intranets worldwide to disseminate information and news to a wide
user base. Educational institutions use VPNs to connect campuses that can be
distributed across the country or around the world.
In order to gain access to the
private network, a user must be authenticated using a unique identification and
a password. An authentication token is often used to gain access to a private
network through a personal identification number (PIN) that a user must enter.
The PIN is a unique authentication code that changes according to a specific frequency,
usually every 30 seconds or so.
VPN creates a tunnel, and all your network and online
activity travels through it. From the point of view of someone else sniffing
around on the same network, your activity is hidden because it is inside that
tunnel. Furthermore, all your data is encrypted, giving you another level of
security.
There are
two types of VPN connections: incoming and outgoing. An outgoing session means
the user is using the computer to remotely connect to some other network or
machine, as may happen when the user is accessing a work computer. If you have
a wireless router at home that supports VPN, you can set up an outgoing
connection from your laptop to connect to the router and get access to your
media server, your home computer, and other devices on your home network
remotely.
An incoming
session means other machines can access your machine. Think carefully before
you grant access to your computer. One scenario where this makes sense is if
you have a lot of media files or documents on the computer that people need to
be able to access at any time.
It is straightforward to set up
either type of connection using the built-in VPN client in Windows 7
Step by step setup a VPN connection:
1. Go
to Network and Sharing Center (under Control Panel, Network and Internet), then
go "Set up a new connection or network. click on "Connect to a
Workplace" in order to start the connection wizard, and then select
"Use my Internet connection (VPN)" option to begin the process.
 |
| minhazurnetwork |
2. In the Internet address field,
enter the IP address of the VPN server or the network's domain name. This
information will usually be provided by the network administrator. If you are
connecting to the home router, then you would put in the IP address of that
router.
The
destination name field displays the name users would see. If you aren't going
to connect right away, select the "Don't connect now; just set it up so I
can connect later" checkbox.
Leaving it
unchecked means the client will try to make a connection at the end of the
wizard. If there are multiple users on the Windows 7 box, you can either check
off "Allow other people to use this connection" to make the VPN
connection available to others, or leave it unchecked to ensure no one else has
the option.
 |
| minhazurnetwork |
3. This screen asks for a username and
password. If you leave it blank, you will be prompted to enter the information
when making the actual connection.
4. The final window, if you selected
"Don't connect now," will display a "Connect now" option.
You can close the window now, or connect.
When you are
ready to connect, just click on the network icon in systray (the icon could be
for the wireless network or for the wired one) and the connection that was
created earlier would show up in the list under "Dial-up and VPN."
You can also get here by clicking on "Connect to a network" under
Network and Sharing Center.
5. In the VPN connection box, enter
the username and password to the VPN network, if it isn't already
pre-populated, along with the domain provided by the administrator. This
connection should work for a majority of VPN networks.
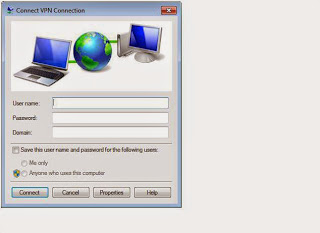 |
| minhazurnetwork |
6. If the
connection fails, click on Properties. The most common issue has to do with the
server configuration. Select the "Security" tab in the Properties
window. Type of VPN" should be set to Automatic. Check with the
administrator if it should be set to PPTP, L2TP/IpSec, SSTP, or IKEv2. If it
still doesn't work, it's possible you should uncheck "Include Windows
logon domain" under the Options tab.
 |
| minhazurnetwork |
7. After
saving the properties, select Connect to launch the connection. You are now
connected to a VPN server and your connection is safe.
No comments:
Post a Comment